Pacman: uses the official manjaro repository to upgrade the package database and all system packages.
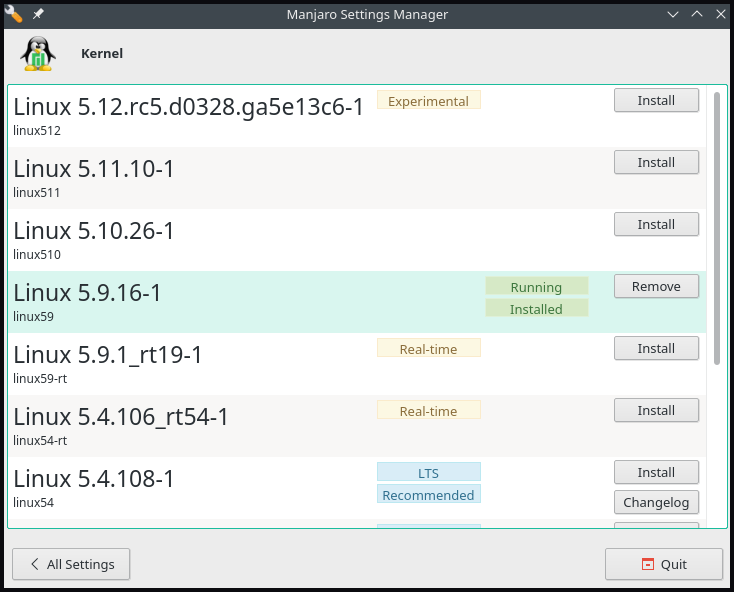
mhwd-kernel: manjaro hardware detection command unique feature that provides easy installation and management of system kernels.
Identify In-Use Kernel
Before beginning the process of kernel version upgrade/downgrade, identify current version details via the mhwd-kernel command:
manjaro@manjaro:~$ mhwd-kernel -liCurrently running: 5.9.16-1-MANJARO (linux59)
The following kernels are installed in your system:
* linux59
The above command outputs the system kernel version, 5.9.16-1-MANJARO, along with the list of installed kernels.
Upgrade Kernel
One of the other distinguishing features of Manjaro is the use and installation of multiple Kernel versions, as well as the user’s access to bleeding-edge kernels.
Use the pacman command to list all the kernel version packages with 5.x and below:
[ manjaro @ manjaro ~ ] $ pacman -Ss linux5* | grep "kernel and modules" The Linux414 kernel and modules
The Linux419 kernel and modules
The Linux44 kernel and modules
The Linux49 kernel and modules
The Linux510 kernel and modules
The Linux511 kernel and modules
The Linux512 kernel and modules
The Linux54 kernel and modules
The Linux59 kernel and modules
The Linux-rt-lts-manjaro kernel and modules
The Linux-rt-manjaro kernel and modules
The Linux54-rt kernel and modules
The Linux59-rt kernel and modules